In class we discussed the idea of a “Human Genome Project 2.0”, but instead of reading DNA, writing DNA. For your homework, please answer each of the following questions:
(1) If humanity were to undertake such a project, what would be the benefits? What types of new science and engineering would be enabled if we had such a synthetic human genome? Please provide specific examples.
(2) Conversely, why might we not want to proceed with such an endeavor? What are the risks?
(3) Map out a technical strategy for synthesizing a human genome. What technologies would be required? What are existing tools we could leverage? For certain tools that do not exist, what should their capabilities be?

The Incredible Shrinking Man (1957)
https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0050539/
1) "It seems as if nature itself is already investigating ways to counter hypergrowth, overpopulation and overconsumption."
The Incredible Shrinking Man :: http://www.the-incredible-shrinking-man.net/
Project by artist Arne Hendriks
In a society that fetishizes the tall, it is often overlooked the wide range of benefits that arise from downsizing the human race. Embracing dwarfism would have many major impacts on the way we live, the amount of energy we consume, even the way we would survive in space (colonizing small asteroids maybe?). Think in entropic terms: human height researcher Thomas T. Samaras states, a smaller person has up to 40 trillion cells less that are subjected to harmful processes and substances and thus have a greater chance at longevity. It’s been suggested that tall people age faster, and therefor die younger since larger body requires more cell doublings due to the ongoing regeneration of tissues over a lifetime.
2) There are many physical complications associated with both proportional and disproportional dwarfism, such as poorly developed organs, heart problems, and Turner syndrome resulting from growth hormone deficiency.
3) In a simple, short answer, we can induce pituitary dwarfism ::
Most dwarfism is caused by the decreased production of hormones, such as growth hormone (anterior pituitary gland) or somatomedin C (liver). On the chromosomal level, there appears to be disruption on different areas of chromosome 3 and 7. Some studies have isolated defects for the production of pituitary hormones to the short arm (the "p" end) of chromosome 3 at a specific location of 3p11. Other studies have found changes on the short arm of chromosome 7.
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Pituitary+Dwarfism
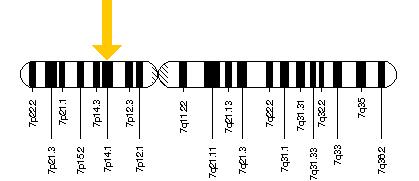
Located on chromosome 7, location 7p14 is the gene growth-hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR). A mutation on this gene has also been associated with dwarfism. The GHRHR is expressed in the pituitary which binds to GHRH released by the hypothalamus, stimulating the pituitary to release growth hormone.
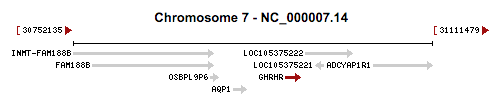

https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2692#
We can potentially use the CRISPR/Cas9 technique to knock out the GHRHR gene on chromosome 7, causing a mutation that leads to dwarfism.